Iron Overload
Iron overload in the inherited globin disorders can result directly from increased iron absorption or from transfusional iron overload. In thalassaemia major, t can be fatal in the second or third decade of life if not treated. In the section on Iron Homeostasis, you learned that hepcidin synthesis is decreased by erythropoiesis. This results in less hepcidin biding to enteric ferroportin, which prevents its degradation. Hence, there is increased absorption of iron from the gastrointestinal tract. This is the basis of iron overload in states of ineffective erythropoiesis.
Clinical Features

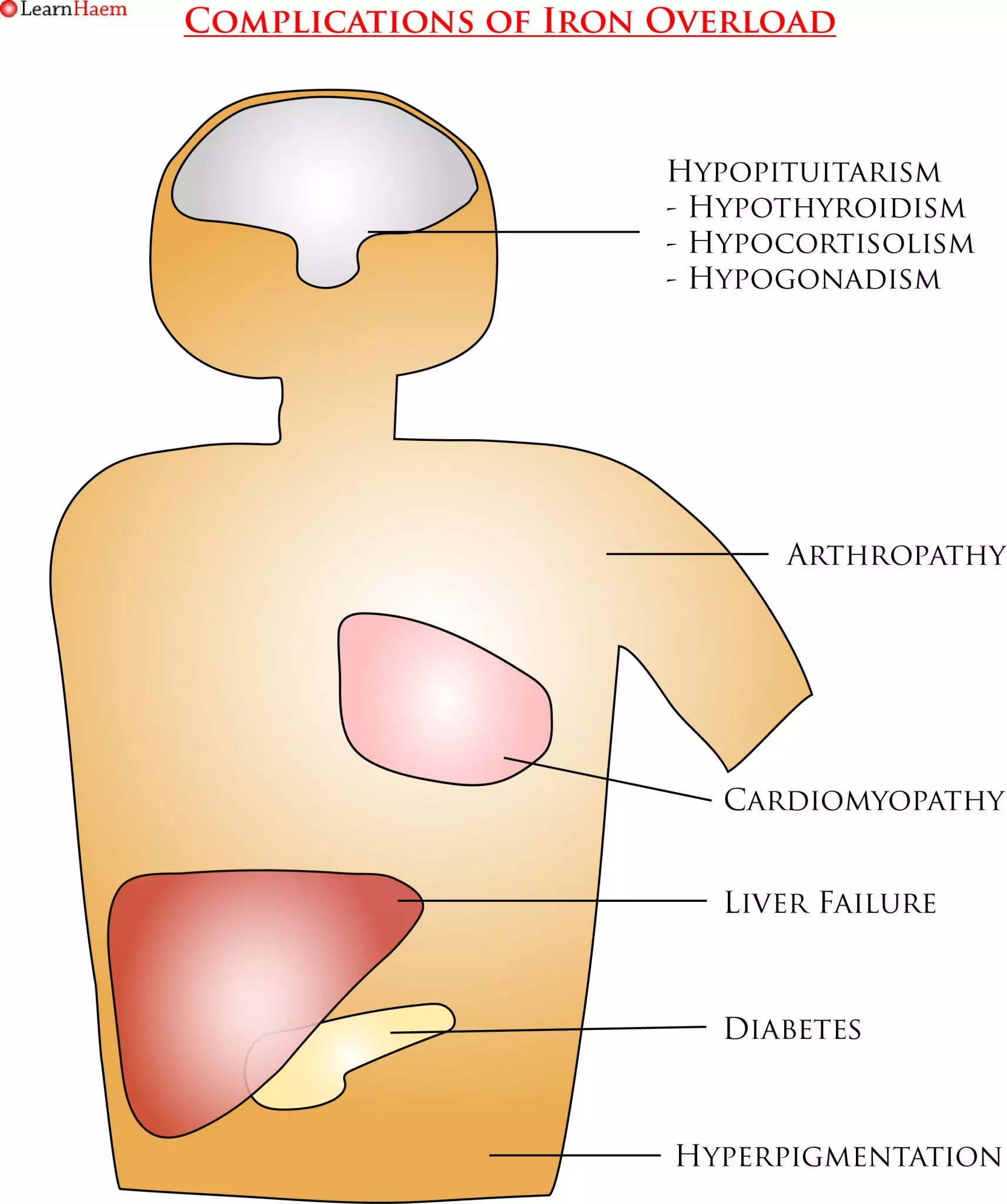
Symptoms of Iron Overload. Iron is deposited in the pituitary gland, skin, heart, liver, pancreas and joints. In the pituitary, it can cause pan-hypopituitarism, resulting in hypothyroidism, hypocortisolism and hypogonadism. In children, a lack of growth hormone results in short stature and delayed or absent puberty. Cardiac and liver iron loading cause progressive cardiomyopathy and cirrhosis. Pancreatic iron loading causes diabetes, while iron in the skin results in hyperpigmentation (hence the name “bronze diabetes”). Iron deposition in the joints can cause significant arthralgia.
Diagnosis
- Serum ferritin is the most commonly used marker of iron overload. However, levels do not correlate with cardiac iron overload, and hence cannot be used to monitor cardiac iron concentration. The test is also highly non-specific. Thalassaemia International Federation guidelines suggest keeping ferritin levels <1000μg/L (or <800μg/L if MRI imaging is not available).
- Liver iron concentration (LIC) measurement is the gold standard test for body iron balance. Normal LIC values are up to 1.8mg/g dry weight; sustained values about 15mg/g dry weight result in progressive fibrosis and cirrhosis. LIC can be measured by biopsy or MRI T2*.
- MRI T2* has been used for cardiac iron assessment. T2* values of <10ms are associated with a very high risk of cardiac failure (160-fold risk over 1 year); patients with values of 10-20ms have mild to moderate myocardial iron loading.

Leave A Comment