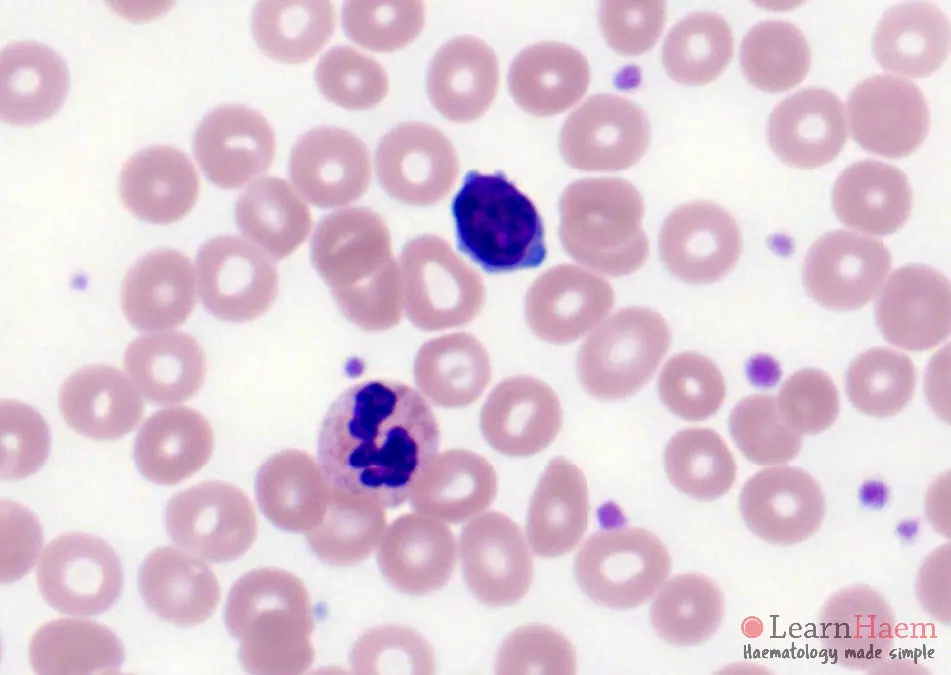
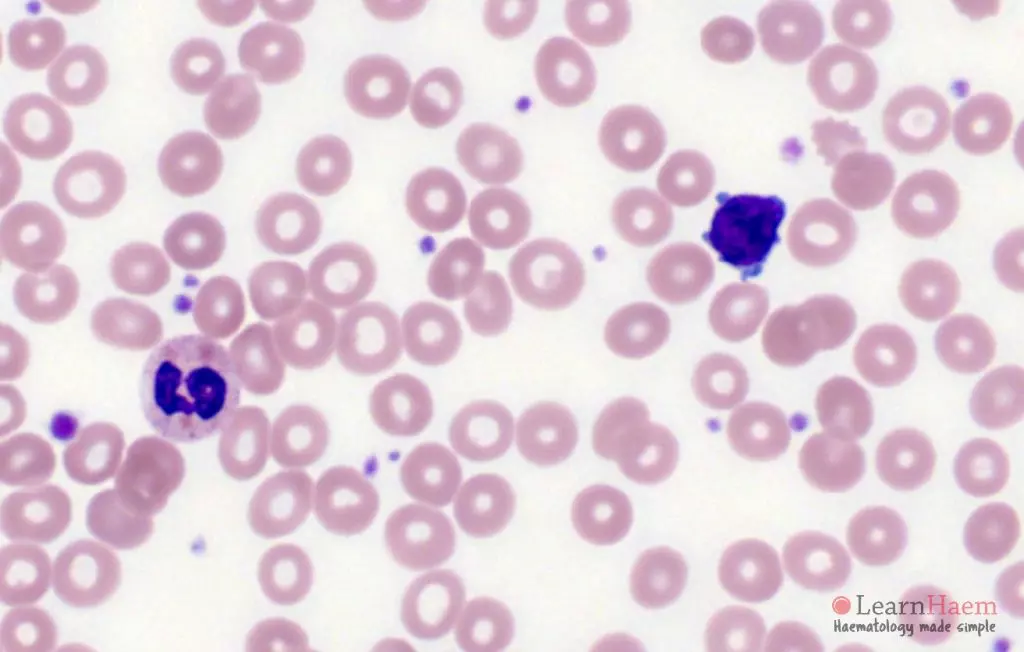
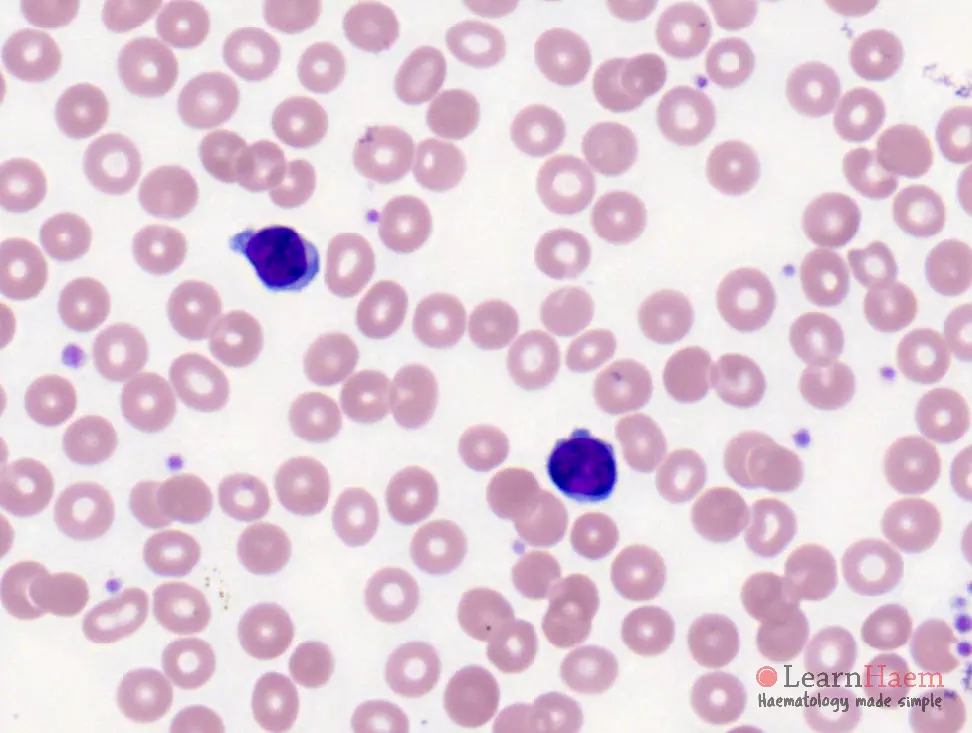
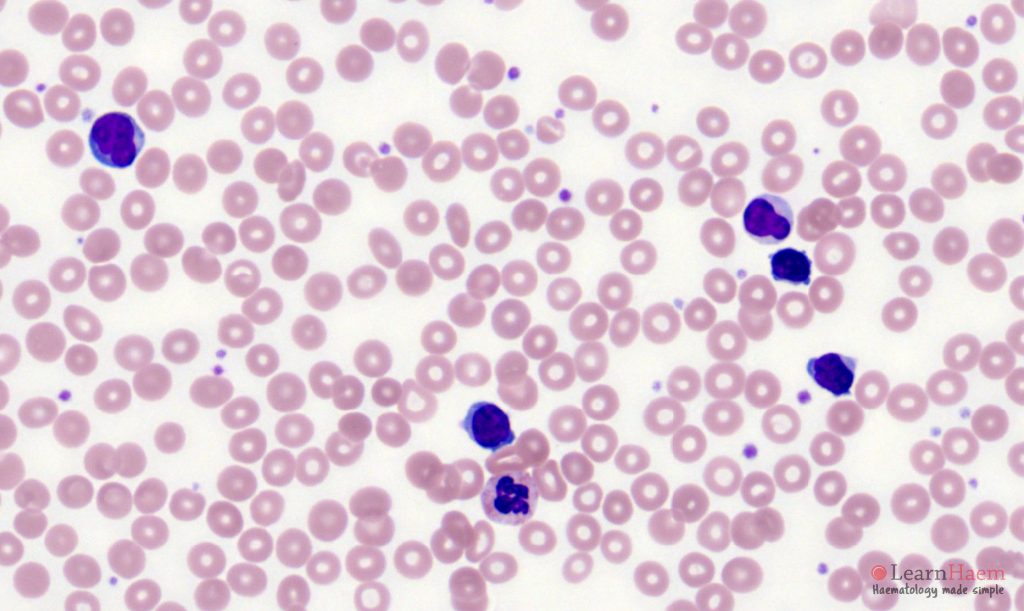
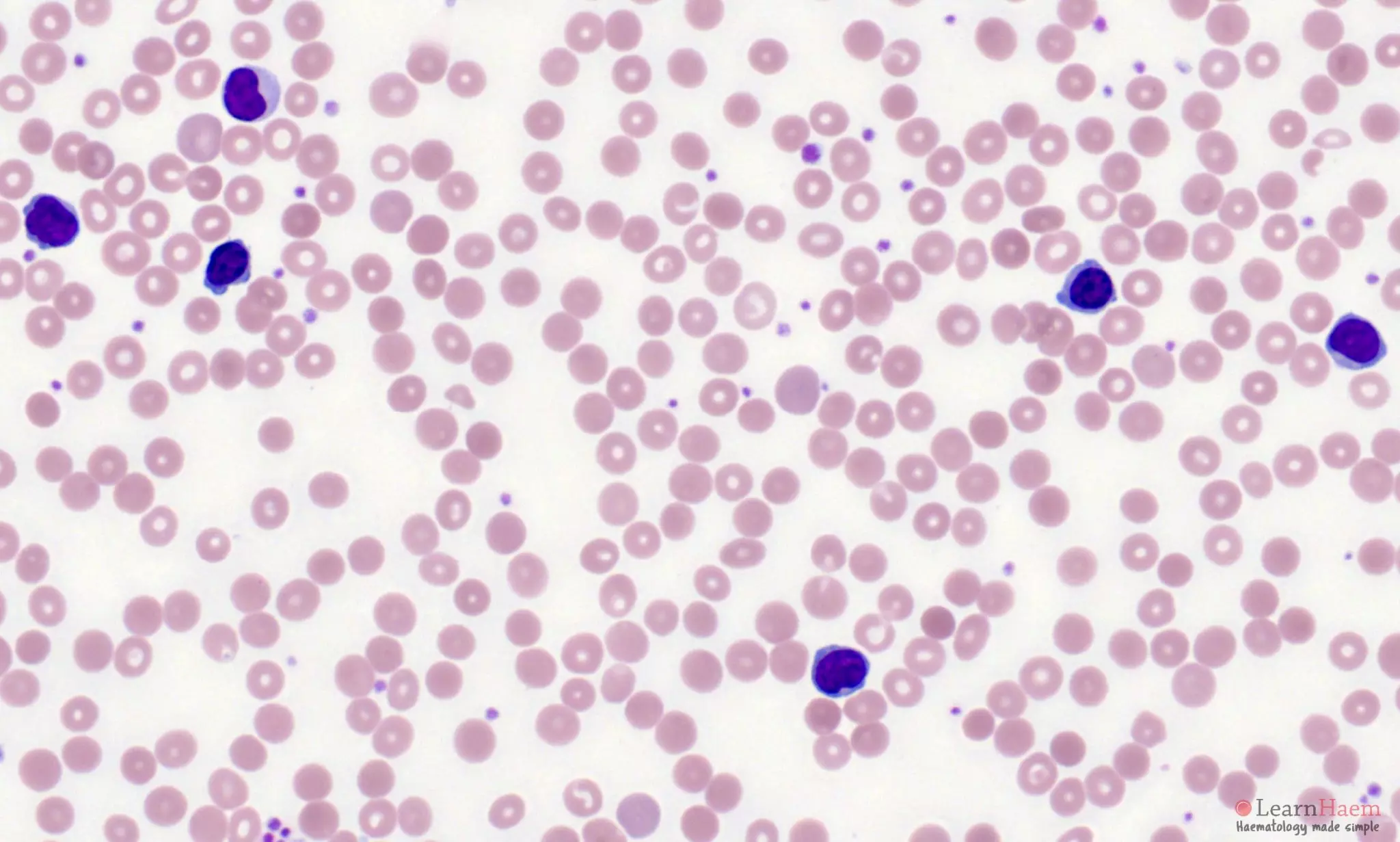
Morphological features
- Usually marked lymphocytosis.
- Atypical lymphoid cells with clumped chromatin
- Single, indistinct nucleolus – may be more apparent at lower magnification.
- Cytoplasmic blebbing is common.
- Minimal basophilic, agranular, cytoplasm.
- Morphological variants (not associated with distinct clinical presentation or outcomes):
- Small cell (20%), nucleoli invisible by light microscopy.
- Sezary (5%) with irregular, cerebriform nuclei.


0 x


0 x


0 x


0 x


0 x


0 x


0 x


0 x


0 x


0 x


0 x
Distinguishing T-PLL from B-PLL
| Feature | B-PLL | T-PLL |
|---|---|---|
| Cytoplasm | Large amounts | Minimal |
| Blebbing | None | Cytoplasmic projections in some cells |
| Nucleoli | Prominent | Subtle and indistinct |
| Size | Large | Small to medium-sized |
| Nuclear outline | Regular | Irregular |
| Immunophenotype | CD20+/19+/SmIg++/22+ CD79a+/23-/5variable | CD3+/2+/5+/7++/1a-/TdT- Typically TCL1+ (>90%) and CD52+ Usually 4+/8- (60%), or 4+/8+ (25%) Characterised by lack of phenotypic aberrancy |
| Cytogenetics | 13q deletion 11q deletion 17p deletion 6q deletion | t(14;14) Inversion 14 Iso8q, trisomy 8, occasionally complex |
Diagnostic Criteria
Requires all three major criteria or two major + one minor criteria.
- Major criteria
- >5 × 109/L cells of T-PLL phenotype in peripheral blood or bone marrow
- T-cell clonality (by PCR for TCR-ß/TCR-Γ, or by flow cytometry)
- Abnormalities of 14q32 or Xq28 OR expression of TCL1A/B, or MTCP1
- Minor criteria
- Abnormalities involving chromosome 11 (11q22.3; ATM)
- Abnormalities in chromosome 8: idic(8)(p11), t(8;8), trisomy 8q
- Abnormalities in chromosome 5, 12, 13, 22, or complex karyotype
- Involvement of T-PLL specific site (eg, splenomegaly, effusions)

Leave A Comment