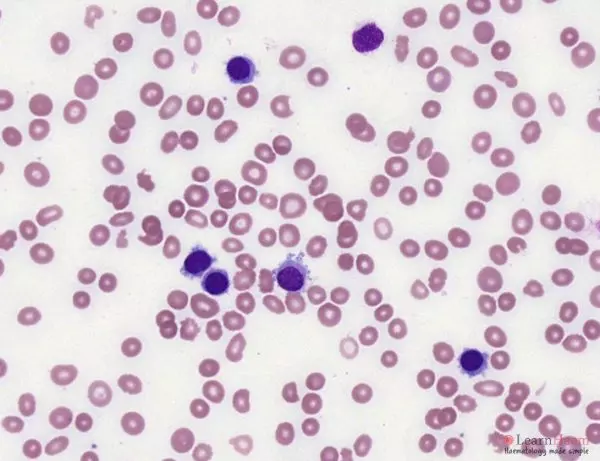
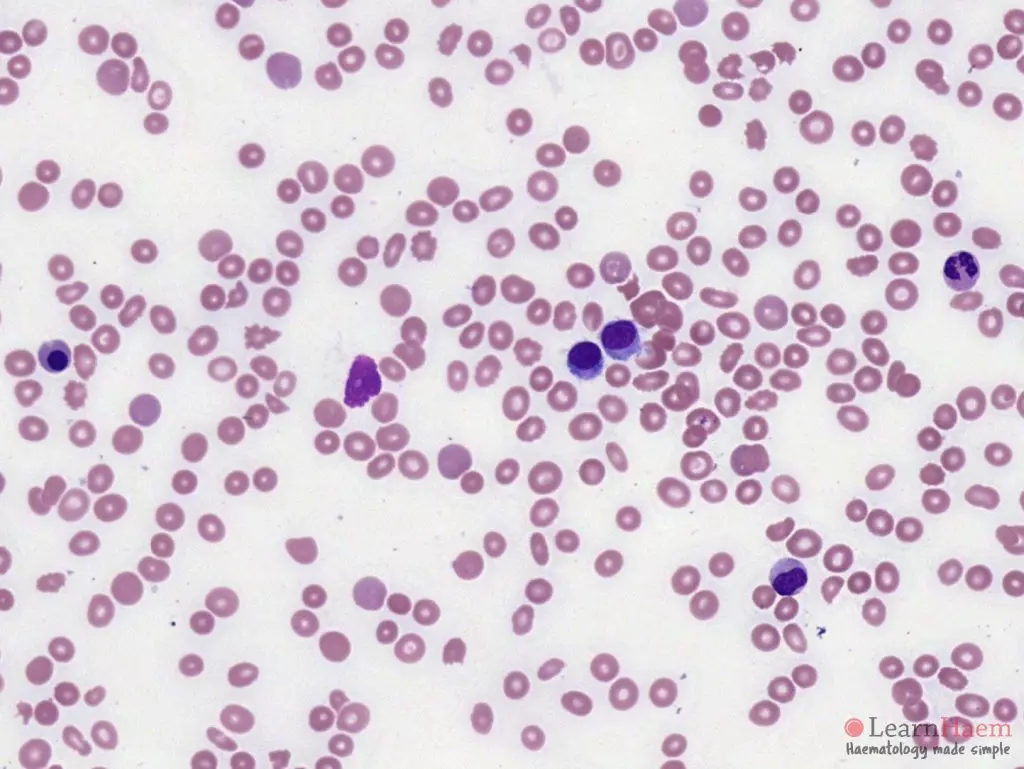
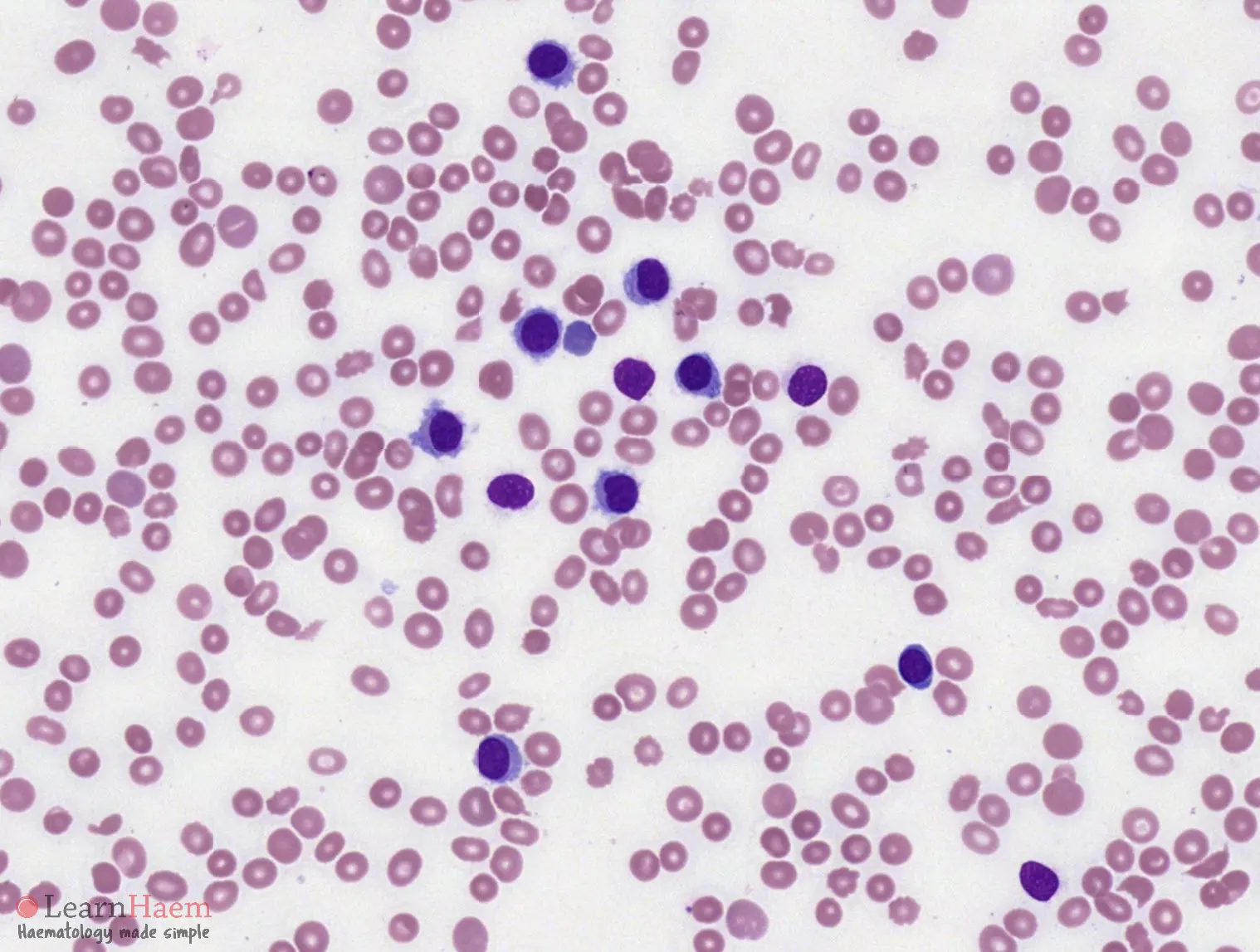
Morphological features:
- Typically pancytopaenic
- Atypical lymphoid cells are larger than normal lymphocytes
- Abundant, weakly-basophilic cytoplasm with irregular projections which are thread-like
- May be easier to see projections in the thicker part of the film
- Nuclear outline is typically regular – round or oval
- Occasionally kidney, dumbbell or bi-lobed
- Generally absent nucleoli
- Monocytopaenia
- Anaemia (usually normocytic)
- There may be a leukoerythroblastic picture and teardrop cells from secondary marrow fibrosis.


0 x


0 x


0 x
Clinical features:
- Splenomegaly
- No lymphadenopathy
- Symptoms and signs of pancytopaenia
Differential diagnosis:
- Marginal zone lymphoma (less cytoplasm which is mor basophilic, no monocytopaenia)
- Hairy cell leukaemia variant (often has prominent nucleoli, no monocytopaenia)
| Disease | Immunophenotype | Other Features |
|---|---|---|
| Hairy cell leukaemia | 20++/11c+/25+/103+/123+ | Annexin A1 positive BRAF positive Monocytopaenia Pancytopaenia |
| Hairy cell variant | 20+/11c+/103+/25-/123- | No monocytopaenia Generally high WBC May have prominent nucleoli BRAF mutation negative Annexin A1 and TRAP negative 50% have TP53 abnormalities and MAP2K1 mutations |
| Splenic marginal zone leukaemia / Splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes | Non-specific B cell phenotype. May be 11c+, occasionally 5+ or 103+. |
Bone marrow aspirate features
- Typically aparticulate.
- In some cases where the secondary marrow fibrosis is not severe, aspirates may show the same atypical lymphoid cells seen in the peripheral blood.


0 x
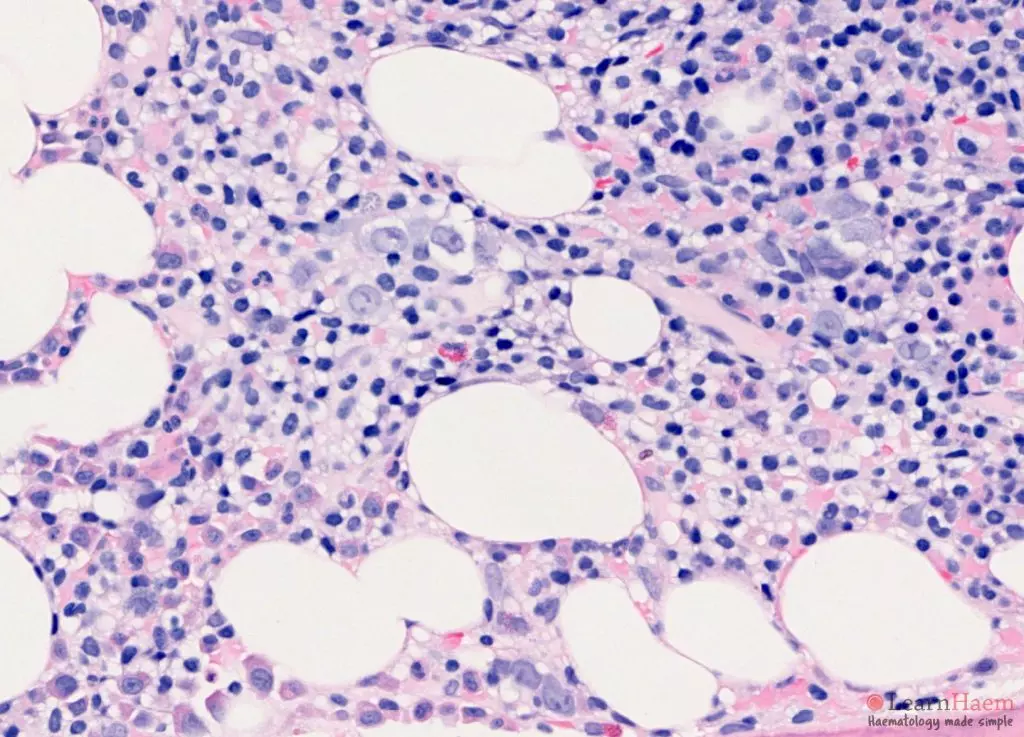
Trephine features
- Variable extent of bone marrow effacement.
- Primary pattern is interstitial or patchy, usually some preservation of fat and haematopoietic elements.
- Characteristic infiltrate with widely-spaced lymphoid cells.
- Abundant cytoplasm and prominent cell borders produce a “fried egg” appearance.
- Mitotic figures are extremely rare.


0 x


0 x


0 x


0 x

Leave A Comment